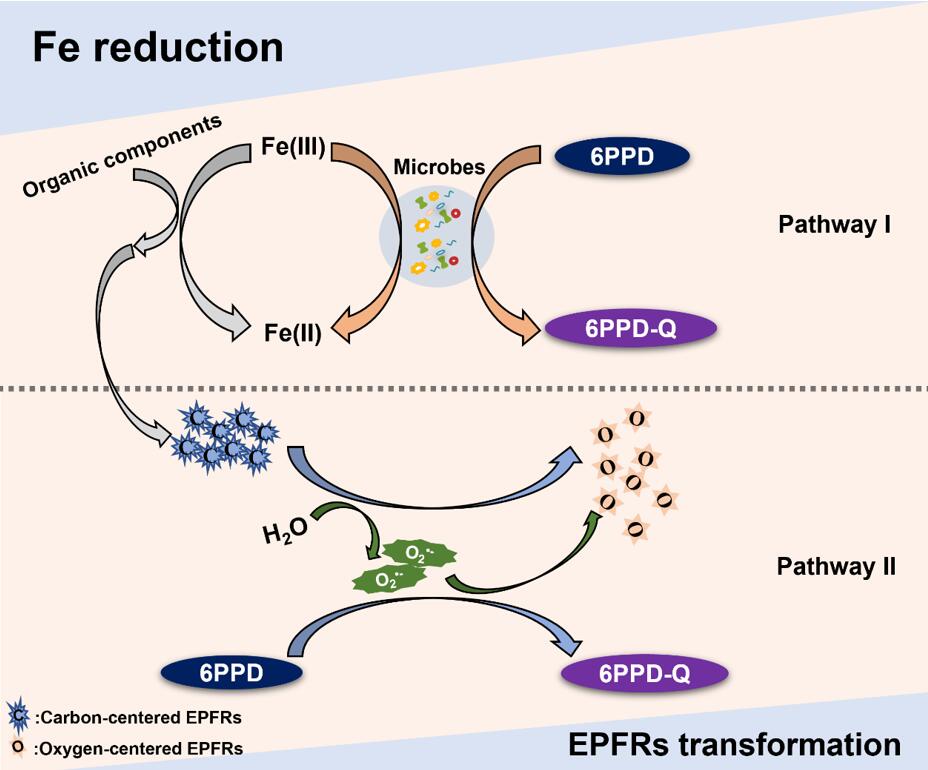
Rapid urbanization drives increased emission of tire wear particles (TWPs) and the contamination of a transformation product derived from tire antioxidant, termed as N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine-quinone (6PPD-Q), with adverse implications for terrestrial ecosystems and human health. However, whether and how 6PPD-Q could be formed during the aging of TWPs in soils remains poorly understood. Here, we examine the accumulation and formation mechanisms of 6PPD-Q during the aging of TWPs in soils. Our results showed that biodegradation predominated the fate of 6PPD-Q in soils, whereas anaerobic flooded conditions were conducive to the 6PPD-Q formation and thus resulted in a ~3.8-fold higher accumulation of 6PPD-Q in flooded soils than wet soils after aging of 60 days. The 6PPD-Q formation in flooded soils was enhanced by Fe reduction-coupled 6PPD oxidation in the first 30 days, while the transformation of TWP-harbored environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs) to superoxide radicals (O2.–) under anaerobic flooded conditions further dominated the formation of 6PPD-Q in the next 30 days. This study provides significant insight into understanding the aging behavior of TWPs and highlights an urgent need to assess the ecological risk of 6PPD-Q in soils.