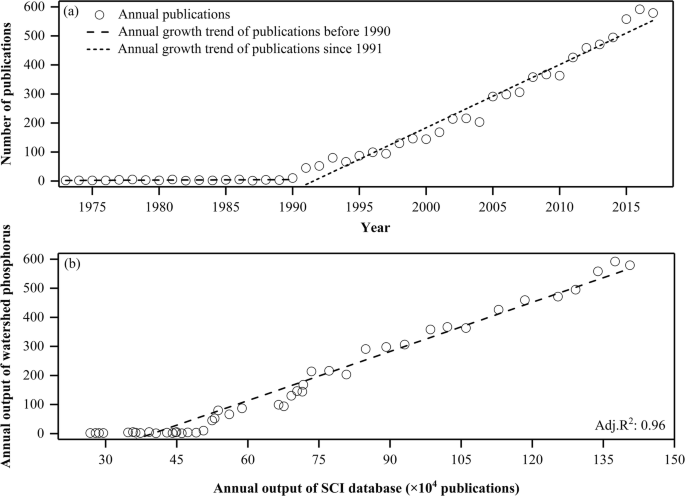
As phosphorus plays a significant role in the maintenance of ecosystem service at watershed scale, it has been studied with a dramatic growth of publications. The bibliometric dataset of publications on watershed phosphorus was downloaded from the Science Citation Index Expanded from the Web of Science and visualized with cluster and network analysis to map global research status and trends. The results showed that annual output of articles experienced a notable increase since 1991. Most research articles on watershed phosphorus appeared in the Journal of Environmental Quality. “Environmental Sciences,” “Water Resources,” and “Marine Freshwater Biology” were the most popular subject categories, and a development tendency of cross-disciplinary research appeared since 2005. The USA was a leading country in total publications, collaborating closely with China, Canada, and the UK. Chinese Academy of Sciences, USDA ARS, and US Geological Survey were the most productive institutions, and Chinese Academy of Sciences has become the core force of international cooperation recently. The mainstream research related to watershed phosphorus was environmental issues like eutrophication. Moreover, phosphorus management using models (soil and water assessment tool and best management practices) has emerged as an important research direction recently. To tackle environmental issues and realize sustainable development of watershed, it is crucial to further strengthen (1) the interdisciplinary collaboration, particularly between natural and social sciences; (2) North–South, South–South, and triangular regional cooperation on science and technology; and (3) theoretical research on the impact of human activities and climate change on biogeochemical cycle of phosphorus and ecosystem integrality of watershed.